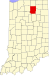
Kosciusko County, Indiana
Kosciusko County | |
|---|---|
 Kosciusko County Courthouse in Warsaw | |
 Location within the U.S. state of Indiana | |
 Indiana's location within the U.S. | |
| Coordinates: 41°14′N 85°52′W / 41.24°N 85.86°W | |
| Country | |
| State | |
| Founded | February 7, 1835 (authorized) 1836 (organized) |
| Named for | Tadeusz Kościuszko |
| Seat | Warsaw |
| Largest city | Warsaw |
| Area | |
• Total | 554.39 sq mi (1,435.9 km2) |
| • Land | 531.38 sq mi (1,376.3 km2) |
| • Water | 23.01 sq mi (59.6 km2) 4.15% |
| Population (2020) | |
• Total | 80,240 |
• Estimate (2023) | 80,364 |
| • Density | 140/sq mi (56/km2) |
| Time zone | UTC−5 (Eastern) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−4 (EDT) |
| Congressional districts | 2nd, 3rd |
| Website | www |
| Indiana county number 43 | |
Kosciusko County (/ˌkɒskiˈʌskoʊ/ KOS-kee-US-koh) is a county in the U.S. state of Indiana. At the 2020 United States Census, its population was 80,240.[1] The county seat (and only incorporated city) is Warsaw.[2] The county was organized in 1836. It was named for the Polish general Tadeusz Kościuszko who served in the American Revolutionary War and then returned to Poland.[3] The county seat is named for Warsaw, the capital of Poland.[4]
History
[edit]The Indiana State Legislature passed an omnibus county bill[5] on February 7, 1835, that authorized the creation of thirteen counties[6] in northeast Indiana, including Kosciusko. The county government was organized beginning in 1836. The county's boundary lines have remained unchanged since 1835.
Geographical features
[edit]Kosciusko County terrain consists of low rolling hills dotted with bodies of water and drainages, with all available area devoted to agriculture or urban development.[7] Its highest point (1025'/312 meters ASL) is a hill NE of Dewart Lake.[8] The Tippecanoe River flows westward through the central part of the county, while the Eel River flows southwestward through the county's SE corner.[7]
According to the 2010 census, the county has a total area of 554.39 square miles (1,435.9 km2), of which 531.38 square miles (1,376.3 km2) (or 95.85%) is land and 23.01 square miles (59.6 km2) (or 4.15%) is water.[9]
Adjacent counties
[edit]- Elkhart County - north
- Noble County - northeast
- Whitley County - southeast
- Wabash County - south
- Fulton County - southwest
- Marshall County - west
Major highways
[edit]Lakes
[edit]- Banning Lake
- Beaver Dam Lake
- Big Barbee Lake
- Big Chapman Lake
- Carr Lake
- Center Lake
- Dewart Lake
- Diamond Lake
- Fish Lake
- Goose Lake
- Hoffman Lake
- Hill Lake
- Irish Lake
- James Lake
- Kuhn Lake
- Lake Wawasee
- Little Barbee Lake
- Little Chapman Lake
- Loon Lake
- McClures Lake
- Muskellunge Lake
- Palestine Lake
- Papakeechie Lake
- Pike Lake
- Ridinger Lake
- Rock Lake (part)
- Sechrist Lake
- Shoe Lake
- Silver Lake
- Stanton Lake
- Syracuse Lake
- Tippecanoe Lake
- Waubee Lake
- Winona Lake
- Yellow Creek Lake[7]
Protected areas
[edit]- Center Lake Wetland Conservation Area
- Edmund and Virginia Ball Nature Preserve
- Pisgah Marsh Nongame Area (part)[7]
City and towns
[edit]Unincorporated communities
[edit]- Atwood
- Barbee
- Bayfield
- Beaver Dam
- Bell Rohr Park
- Buttermilk Point
- Cedar Point
- Clunette
- DeFries Landing
- Enchanted Hills
- Forest Glen
- Gravelton
- Hastings
- Highbanks
- Highlands Park
- Island Park
- Kalorama Park
- Kanata Manayunk
- Kinsey
- Lakeside Park
- Lakeview Spring
- Lowman Corner
- Marineland Gardens
- Milford Junction
- Mineral Springs
- Monoquet
- Musquabuck Park
- Oakwood Park
- Osborn Landing
- Oswego
- Packerton
- Palestine
- Pickwick Park
- Potawatomi Park
- Redmon Park
- Sevastopol
- Shady Banks
- South Park
- Stoneburner Landing
- Stony Ridge
- Vawter Park
- Walker Park
- Wawasee
- Wawasee Village
- Wooster
- Yellowbanks
Townships
[edit]Climate and weather
[edit]| Warsaw, Indiana | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Climate chart (explanation) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
In recent years, average temperatures in Warsaw have ranged from a low of 15 °F (−9 °C) in January to a high of 82 °F (28 °C) in July, although a record low of −25 °F (−32 °C) was recorded in January 1985 and a record high of 103 °F (39 °C) was recorded in July 1976. Average monthly precipitation ranged from 1.45 inches (37 mm) in February to 4.51 inches (115 mm) in June.[10]
Community
[edit]
Newspapers
[edit]Radio Stations
[edit]Government
[edit]The county government is a constitutional body, and is granted specific powers by the Constitution of Indiana, and by the Indiana Code.
County Council: The legislative branch of the county government; controls spending and revenue collection in the county. Representatives, elected to four-year terms from county districts, are responsible for setting salaries, the annual budget, and special spending. The council has limited authority to impose local taxes, in the form of an income and property tax that is subject to state level approval, excise taxes, and service taxes.[11][12]
Board of Commissioners: The executive body of the county; commissioners are elected countywide to staggered four-year terms. One commissioner serves as president. The commissioners execute the acts legislated by the council, collect revenue, and manage the county government.[11][12]
Court: The county maintains a small claims court that handles civil cases. The county also maintains a Circuit and Superior Court. The judge on each court is elected to a term of six years and must be a member of the Indiana bar.
County Officials: The county has other elected offices, including sheriff, coroner, auditor, treasurer, recorder, surveyor, and circuit court clerk. The officials are elected countywide to four-year terms. Members elected to county government positions are required to declare party affiliations and to be residents of the county.[12]
Kosciusko County is part of Indiana's 2nd and 3rd congressional districts. It is also part of Indiana Senate districts 9, 13, 17 and 18[13] and Indiana House of Representatives districts 18, 22 and 23.[14]
Elected officials:
- Jim Smith - Sheriff
- Daniel Hampton - Prosecutor
- Susan Engelberth - Assessor
- Michelle Puckett - Auditor
- Ann Torpy - Clerk
- Joetta Mitchell - County Recorder
- Sue Ann Mitchell - Treasurer
- Cary P. Groninger - Middle District Commissioner
- Robert M. Conley, President - Southern District Commissioner
- Bradford Jackson - Northern District Commissioner
- Tony Ciriello, Certified Death Investigator, Coroner
Kosciusko County is a Republican stronghold in presidential elections. Woodrow Wilson in 1912 and Franklin D. Roosevelt in 1932 are the only two Democratic Party candidates to win the county from 1888 to the present day. Roosevelt is the only Democrat since 1888 to win the county with a majority. The county is very Republican even by the standards of traditionally Republican Indiana. For example, Roosevelt actually lost the county by eight percentage points in 1936 even as he went on to carry 46 states. Further underlining the county's Republican bent, it rejected Lyndon Johnson in 1964 even in the midst of Johnson's 44-state national landslide. Johnson is the last Democrat to manage even 40 percent of the county's vote.
| Year | Republican | Democratic | Third party(ies) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | % | No. | % | No. | % | |
| 2024 | 26,213 | 74.88% | 7,995 | 22.84% | 798 | 2.28% |
| 2020 | 26,499 | 73.85% | 8,364 | 23.31% | 1,021 | 2.85% |
| 2016 | 23,935 | 73.78% | 6,313 | 19.46% | 2,193 | 6.76% |
| 2012 | 22,558 | 74.84% | 6,862 | 22.77% | 720 | 2.39% |
| 2008 | 20,488 | 67.87% | 9,236 | 30.60% | 461 | 1.53% |
| 2004 | 22,136 | 78.05% | 5,977 | 21.08% | 247 | 0.87% |
| 2000 | 19,040 | 75.30% | 5,785 | 22.88% | 459 | 1.82% |
| 1996 | 15,084 | 62.99% | 6,166 | 25.75% | 2,695 | 11.25% |
| 1992 | 14,179 | 57.44% | 5,307 | 21.50% | 5,197 | 21.05% |
| 1988 | 17,761 | 76.68% | 5,321 | 22.97% | 81 | 0.35% |
| 1984 | 17,560 | 77.88% | 4,877 | 21.63% | 110 | 0.49% |
| 1980 | 15,633 | 68.78% | 5,684 | 25.01% | 1,413 | 6.22% |
| 1976 | 14,505 | 65.56% | 7,328 | 33.12% | 291 | 1.32% |
| 1972 | 16,216 | 78.93% | 4,233 | 20.60% | 96 | 0.47% |
| 1968 | 12,633 | 63.98% | 5,342 | 27.06% | 1,769 | 8.96% |
| 1964 | 10,488 | 54.10% | 8,759 | 45.18% | 141 | 0.73% |
| 1960 | 13,539 | 69.11% | 5,839 | 29.80% | 213 | 1.09% |
| 1956 | 12,777 | 71.68% | 4,904 | 27.51% | 143 | 0.80% |
| 1952 | 11,521 | 68.95% | 4,677 | 27.99% | 512 | 3.06% |
| 1948 | 9,327 | 62.79% | 5,102 | 34.35% | 426 | 2.87% |
| 1944 | 9,577 | 65.11% | 4,865 | 33.08% | 266 | 1.81% |
| 1940 | 9,879 | 62.68% | 5,768 | 36.60% | 113 | 0.72% |
| 1936 | 8,182 | 53.90% | 6,890 | 45.39% | 107 | 0.70% |
| 1932 | 7,063 | 47.75% | 7,475 | 50.54% | 253 | 1.71% |
| 1928 | 7,973 | 63.18% | 4,537 | 35.95% | 110 | 0.87% |
| 1924 | 6,819 | 58.33% | 4,384 | 37.50% | 487 | 4.17% |
| 1920 | 8,326 | 61.66% | 4,836 | 35.81% | 342 | 2.53% |
| 1916 | 4,025 | 51.18% | 3,447 | 43.83% | 393 | 5.00% |
| 1912 | 1,767 | 24.47% | 2,817 | 39.02% | 2,636 | 36.51% |
| 1908 | 4,377 | 54.45% | 3,362 | 41.82% | 300 | 3.73% |
| 1904 | 4,550 | 57.88% | 2,913 | 37.06% | 398 | 5.06% |
| 1900 | 4,422 | 56.27% | 3,265 | 41.54% | 172 | 2.19% |
| 1896 | 4,342 | 55.61% | 3,372 | 43.19% | 94 | 1.20% |
| 1892 | 3,823 | 53.24% | 3,064 | 42.67% | 294 | 4.09% |
| 1888 | 4,147 | 55.81% | 3,081 | 41.46% | 203 | 2.73% |
Airports
[edit]- KASW - Warsaw Municipal Airport
- KC03 - Nappanee Municipal Airport[16]
Education
[edit]School districts
[edit]Demographics
[edit]| Census | Pop. | Note | %± |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1840 | 4,170 | — | |
| 1850 | 10,243 | 145.6% | |
| 1860 | 17,418 | 70.0% | |
| 1870 | 23,531 | 35.1% | |
| 1880 | 26,494 | 12.6% | |
| 1890 | 28,645 | 8.1% | |
| 1900 | 29,109 | 1.6% | |
| 1910 | 27,936 | −4.0% | |
| 1920 | 27,120 | −2.9% | |
| 1930 | 27,488 | 1.4% | |
| 1940 | 29,561 | 7.5% | |
| 1950 | 33,002 | 11.6% | |
| 1960 | 40,373 | 22.3% | |
| 1970 | 48,127 | 19.2% | |
| 1980 | 59,555 | 23.7% | |
| 1990 | 65,294 | 9.6% | |
| 2000 | 74,057 | 13.4% | |
| 2010 | 77,358 | 4.5% | |
| 2020 | 80,240 | 3.7% | |
| 2023 (est.) | 80,364 | [17] | 0.2% |
| US Decennial Census[18] 1790-1960[19] 1900-1990[20] 1990-2000[21] 2010-2013[22] 2020[1] | |||
As of the 2010 United States Census, there were 77,358 people, 29,197 households, and 20,740 families in the county.[23] The population density was 145.6 inhabitants per square mile (56.2/km2). There were 37,038 housing units at an average density of 69.7 per square mile (26.9/km2).[9] The racial makeup of the county was 93.3% white, 0.8% Asian, 0.7% black or African American, 0.3% Native American, 3.4% from other races, and 1.4% from two or more races. Those of Hispanic or Latino origin made up 7.3% of the population.[23] In terms of ancestry, 33.5% were German, 11.5% were Irish, 10.8% were English, and 8.2% were American.[24]
Of the 29,197 households, 33.9% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 56.6% were married couples living together, 9.5% had a female householder with no husband present, 29.0% were non-families, and 23.9% of all households were made up of individuals. The average household size was 2.60 and the average family size was 3.07. The median age was 37.7 years.[23]
The median income for a household in the county was $47,697 and the median income for a family was $56,305. Males had a median income of $44,358 versus $29,320 for females. The per capita income for the county was $24,019. About 7.0% of families and 10.0% of the population were below the poverty line, including 13.5% of those under age 18 and 5.2% of those age 65 or over.[25]
Notable residents
[edit]- Ambrose Bierce, Civil War veteran, author, newspaper columnist
- Chris Schenkel, former Sportscaster for ABC Sports. Resided in Leesburg, Indiana.[26]
- Rick Fox, retired NBA player. Resided in Warsaw, Indiana.
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ a b 2020 Population and Housing State Data | Indiana
- ^ "Find a County". National Association of Counties. Archived from the original on May 31, 2011. Retrieved June 7, 2011.
- ^ Gannett, Henry (1905). The Origin of Certain Place Names in the United States. Government Printing Office. p. 177.
- ^ De Witt Clinton Goodrich & Charles Richard Tuttle (1875). An Illustrated History of the State of Indiana. Indiana: R. S. Peale & Co. p. 563.
- ^ John W Tyndall & OE Lesh, Standard history of Adams and Wells Counties, Indiana. pp. 284-6 (accessed 9 August 2020)
- ^ The counties are Dekalb, Fulton, Jasper, Jay, Kosciusko, Marshall, Newton, Porter, Pulaski, Stark, Steuben, Wells, and Whitley. Newton County was merged with Jasper County in 1839, and was re-authorized as a separate county in 1859.
- ^ a b c d Kosciusko County IN (Google Maps, accessed 30 July 2020)
- ^ Kosciusko County High Point, Indiana (PeakBagger.com, accessed 30 July 2020)
- ^ a b "Population, Housing Units, Area, and Density: 2010 - County". US Census Bureau. Archived from the original on February 12, 2020. Retrieved July 10, 2015.
- ^ a b "Monthly Averages for Warsaw IN". The Weather Channel. Retrieved January 27, 2011.
- ^ a b Indiana Code. "Title 36, Article 2, Section 3". IN.gov. Retrieved September 16, 2008.
- ^ a b c Indiana Code. "Title 2, Article 10, Section 2" (PDF). IN.gov. Retrieved September 16, 2008.
- ^ "Indiana Senate Districts". State of Indiana. Retrieved July 14, 2011.
- ^ "Indiana House Districts". State of Indiana. Retrieved July 14, 2011.
- ^ Leip, David. "Atlas of US Presidential Elections". uselectionatlas.org. Retrieved May 17, 2018.
- ^ Nappanee Municipal Airport, Nappanee IN (Google Maps, accessed 30 July 2020)
- ^ "Annual Estimates of the Resident Population for Counties: April 1, 2020 to July 1, 2023". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved April 2, 2024.
- ^ "US Decennial Census". US Census Bureau. Retrieved July 10, 2014.
- ^ "Historical Census Browser". University of Virginia Library. Retrieved July 10, 2014.
- ^ "Population of Counties by Decennial Census: 1900 to 1990". US Census Bureau. Retrieved July 10, 2014.
- ^ "Census 2000 PHC-T-4. Ranking Tables for Counties: 1990 and 2000" (PDF). US Census Bureau. Retrieved July 10, 2014.
- ^ "Kosciusko County QuickFacts". US Census Bureau. Archived from the original on June 7, 2011. Retrieved September 25, 2011.
- ^ a b c "Profile of General Population and Housing Characteristics: 2010 Demographic Profile Data". US Census Bureau. Archived from the original on February 13, 2020. Retrieved July 10, 2015.
- ^ "Selected Social Characteristics in the US – 2006-2010 American Community Survey 5-Year Estimates". US Census Bureau. Archived from the original on February 14, 2020. Retrieved July 10, 2015.
- ^ "Selected Economic Characteristics – 2006-2010 American Community Survey 5-Year Estimates". US Census Bureau. Archived from the original on February 14, 2020. Retrieved July 10, 2015.
- ^ (clunette.com/Schenkel)
External links
[edit]- Kosciusko County
- Kosciusko County Chamber of Commerce
- Kosciusko County Convention and Visitors Bureau